For my first blog and dive into the world of information security I choose to use my blog to summarize the week of learning's for each of our 10 weeks. Because I am not a cybersecurity student but pursuing a masters focusing on healthcare and technology I choose a more broad and high level approach for this blog. My weekly blogging helped me solidify each week by focusing on:
- Security and Project Management
- Strategic Planning and Governance
- Contingency and Incident Planning
- Information Security Policy Development
- Security Training and Awareness
- Metrics and Process Measurement
- Risk Management Cycle
- Tools and Strategy to Control Risk
- Technology Strategy for Information Security
- Roles in Information Security
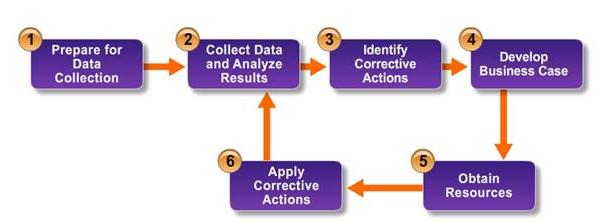
I did rely heavily on three sources for information: our text book, SANS.org and NIST documentation. I also supplemented that with Google images to find appropriate graphs and pictures as I truly believe that a picture is worth a thousand words.
I think this blog could be very interesting to someone like me looking for a broad base and understanding of information security methodologies and how to apply these to the broader information technology arena.